Blockchain
If you’ve heard about blockchain (and who hasn’t recently), you’ve probably heard about it in relation to cryptocurrency, the most prominent example being Bitcoin.
That’s because blockchain is the underlying technological architecture to Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. However, blockchain as a technology has uses that extend beyond cryptocurrency.
What is Blockchain?
Blockgeeks explains it with this simple analogy: “Picture a spreadsheet that is duplicated thousands of times across a network of computers. Then imagine that this network is designed to regularly update this spreadsheet and you have a basic understanding of the blockchain.”
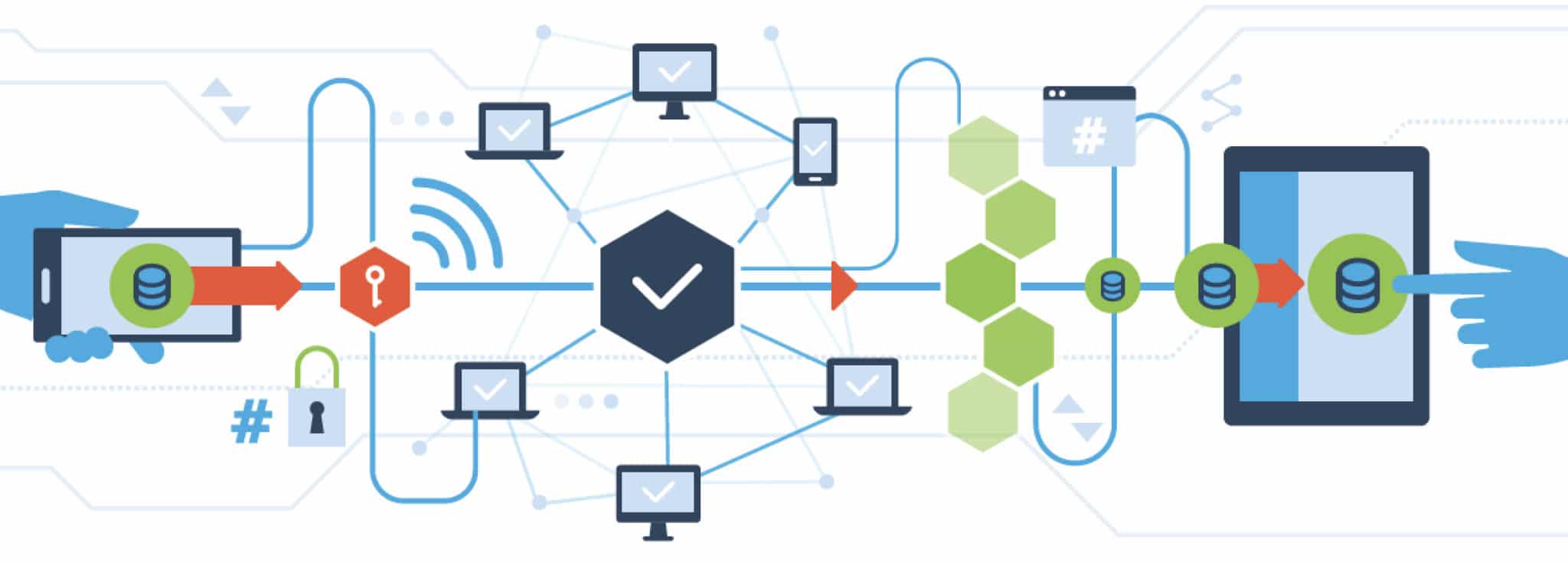
Blockchain is a database that doesn’t allow records to be changed once they are created. If data changes, instead of updating the record, you add another block of data to the chain. In this way, the database relies on a decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) network, shared ledger and public key cryptography (which, in summation, results in complete transparency because authenticity can be verified and every action is marked with a digital signature). Because data stored via blockchain cannot be deleted or breached, it is a much safer way to store highly sensitive data than traditional databases. There are downsides to such databases that will need to be considered as the technology gains popularity, including the size, speed and cost. Blockchain has many applications across a range of industries. Finance, law and real estate all stand to benefit.
Could Blockchain Change Healthcare?
Blockchain offers an accessible, auditable and secure way to store complex data, creating a number of meaningful implications for healthcare. The blockchain transformation won’t happen overnight. But it’s worth understanding how it might change healthcare on both the consumer and administrative fronts.
Blockchain and Provider Data Management and Credentialing
Because blockchain provides greater interoperability and more secure data storage, it has implications for many different aspects of healthcare, including the administrative side of the industry.
The Benefits of Blockchain to Data Storage and Management
Blockchain newbies might be wondering how exactly blockchain is better than other data storage tools. Data storage and management can be improved via blockchain.
There are numerous advantages:
- Data portability.
- Stronger security than traditional databases. An excellent tool for digital data rights management (DRM)—this is why content creation companies like Sony are implementing blockchain. Data owners (in this case, the provider) are able to exercise full control over who accesses data.
- Accessing blockchain data requires immutable authenticity consistent with legal regulations on healthcare records— blockchain creates a record every time data is accessed, so data access histories will be fully transparent.
- Less redundancy in records.
- Blockchain can handle a large volume of data from numerous sources with efficiency, even when multiple parties are accessing the same data source.
- Records will be more accurate— there won’t be confusion between multiple John Smiths, for example, or when a provider’s name changes from Joan Smith to Joan Jones, data continuity will remain.
How Blockchain Could Impact Provider Data Management
Right now, provider data management is organization centric, not data centric or provider centric. In order to share, collect, store and access data, payers, providers and provider organizations use disparate software. It’s not news that this software misalignment causes industry-wide issues with data access, accuracy and therefore usefulness. Each time a provider needs to share their data with a payer or a provider organization, there is no efficient way to do so. Blockchain has the potential to move data management to a data-centric and provider-centric model. By doing so, provider data management can be enhanced at the organization level and healthcare system level.
Use of blockchain technology could eliminate this redundancy throughout the system. Primary source verification (PSV) could become highly transparent and efficient while guaranteeing the authenticity of each piece of data.
Blockchain and Provider Credentialing
Credentialing as we know it could also change. Right now there is redundancy throughout the system: the same provider is credentialed multiple times a year on different schedules at numerous payer and provider organizations. This burdens providers in that it takes them away from providing care to patients and increases admin tasks that lead to burnout. For payers and provider organizations, this can cause extra administrative work, delays and even backlogs. Use of blockchain technology could eliminate this redundancy throughout the system. Primary source verification (PSV) could become highly transparent and efficient while guaranteeing the authenticity of each piece of data. Blockchain may sound confusing at the outset—especially when only known from a Bitcoin perspective—but once you dig into the details, it’s clear that it offers potential meaningful value to the administration of healthcare.
What This Means, in Brief
Payers:
A move to blockchain technology could reduce costs associated with collecting data, including manual people-dependent work and data inaccuracy, which affects downstream processes (e.g., claims and provider directories).
Provider Organizations:
Provider organizations can benefit from the same reduction in admin costs as payers. They will be able to onboard providers faster (getting them off the proverbial bench), allowing them to recognize revenue more quickly.
Providers:
Providers would see less administrative “paperwork” if there is an industry shift that allows for decreased frequency. Even if that takes longer to achieve, they’ll still benefit from easier access, shareability and more control over each piece of data.
Patients:
Patients will see fewer unexpected costs due to a provider falling out of network because of credentialing issues and backlogs. Conversely, this means they should also have access to more providers.